Riboflavin Vitamin B2 CAS 83-88-5 Biochemistry Nutritional Supplement Water Soluble B Yellow To Oran
Riboflavin Vitamin B2 |
CAS No.: 83-88-5 |
Purity: 99% |
Molecular weight: 376.36 g/mol |
Molecular formula: C17H20N4O6 |
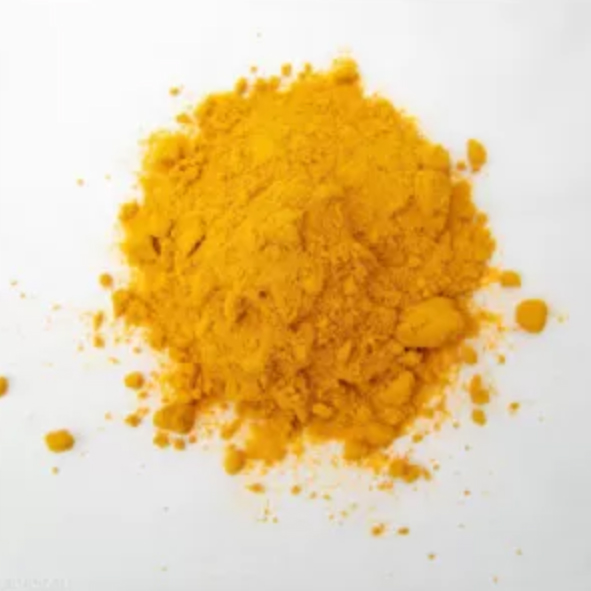
Appearance:Yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder |
Package: 1g,10g,100g,1000g |

Riboflavin Vitamin B2 CAS 83-88-5 Biochemistry Nutritional Supplement Water Soluble B Yellow To Oran
CAS:83-88-5
Purity:99%
Color:Yellow to orange
Form:powder
Deja un mensaje
¡Te llamaremos pronto!
Querida,
Estoy interesado en Riboflavin Vitamin B2 CAS 83-88-5 Biochemistry Nutritional Supplement Water Soluble B Yellow To Oran, podría enviarme más detalles como tipo, tamaño, MOQ, material, etc.
¡Gracias!
Esperando su respuesta.
99% cas 83 88 5
,Vitamin cas 83 88 5
,83 88 5 Riboflavin Vitamin B2
Riboflavin Vitamin B2 CAS 83-88-5 Biochemistry Nutritional supplement Water soluble B Yellow to orange powder
Description:
A water-soluble B fraction was found in the 1920s to contain a yellow, fluorescent growth factor called riboflavin in England and vitamin G in the United States. In the early 1930s, several groups found the coenzyme forms of riboflavin 50-phosphate (flavin mononucleotide) and the further conjugate with adenylic acid (flavin adenine dinucleotide).
Chemical Formula:
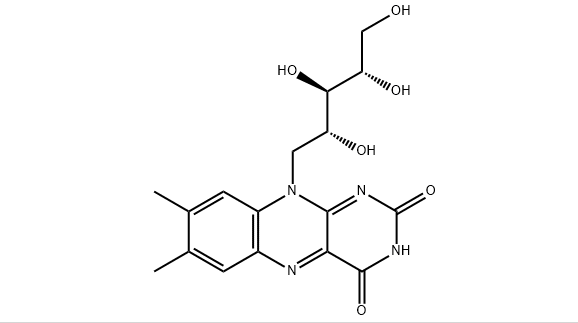
Basic parameters:
| MW | 376.36 |
| Melting point | 290 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Stability | Stable, but light-sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, reducing agents, bases, calcium, metallic salts. May be moisture sensitive. |
| Water solubility | 0.07 g/L (20 ºC) |
Uses:
Riboflavin is the water-soluble vitamin b2 required for healthy skin and the building and maintaining of body tissues. it is a yellow to orange-yellow crystalline powder. it acts as a coenzyme and carrier of hydrogen. it is stable to heat but may dissolve and be lost in cooking water. it is relatively stable to storage. sources include leafy vegetables, cheese, eggs, and milk.
Biochem actions:
Riboflavin serves as a precursor for the active enzyme cofactors riboflavin 5′-monophosphate (also called flavin mononucleotide or FMN) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Riboflavin deficiency in the diet results in a well-defined syndrome known as ariboflavinosis, Riboflavin exhibits protective effects against tumor development and cardiovascular disease. Its deficiency often affects metabolism involving redox reactions. Riboflavin is found essential for iron absorption, gastrointestinal development, neurogenesis, corneal vascularization and corneal opacity.
In which food vitamin B2 is found?
Foods that are particularly rich in riboflavin include eggs, organ meats (kidneys and liver), lean meats, and milk [2,4]. Some vegetables also contain riboflavin. Grains and cereals are fortified with riboflavin in the United States and many other countries [4].
Is it safe to take vitamin B2 everyday?
When taken by mouth: Riboflavin is likely safe for most people in doses of up to 400 mg daily.
How can I increase my B2 vitamin?
You can get recommended amounts of riboflavin by eating a variety of foods, including the following:
Eggs, organ meats (such as kidneys and liver), lean meats, and low-fat milk.
Some vegetables (such as mushrooms and spinach)
Fortified cereals, bread, and grain products.
Should I take B2 in the morning or at night?
You can take any of these water soluble vitamins at any time of the day, but it's often recommended that you take B vitamins in the morning because they help with nutrient metabolism and energy production.
What are the side effects of taking B2?
Side effects that you should report to your care team as soon as possible: Allergic reactions—skin rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
What is the best way to absorb B2?
Riboflavin is best absorbed when taken between meals. People who do not eat a balanced diet every day may benefit from taking a multivitamin and mineral complex.
Is vitamin B2 good for memory?
Vitamin B2 is a crucial ingredient for producing Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) or, in common terms, brain energy. Vitamin B3 has been show to reverse memory loss in mice. In humans, it is used to help the brain repair DNA.
References:
https://ods.od.nih.gov
https://www.webmd.com
https://ods.od.nih.gov
https://batonrougeclinic.com
https://my.clevelandclinic.org
https://www.mountsinai.org
https://www.sabalpalmsseniorliving.com
Recommended Products












